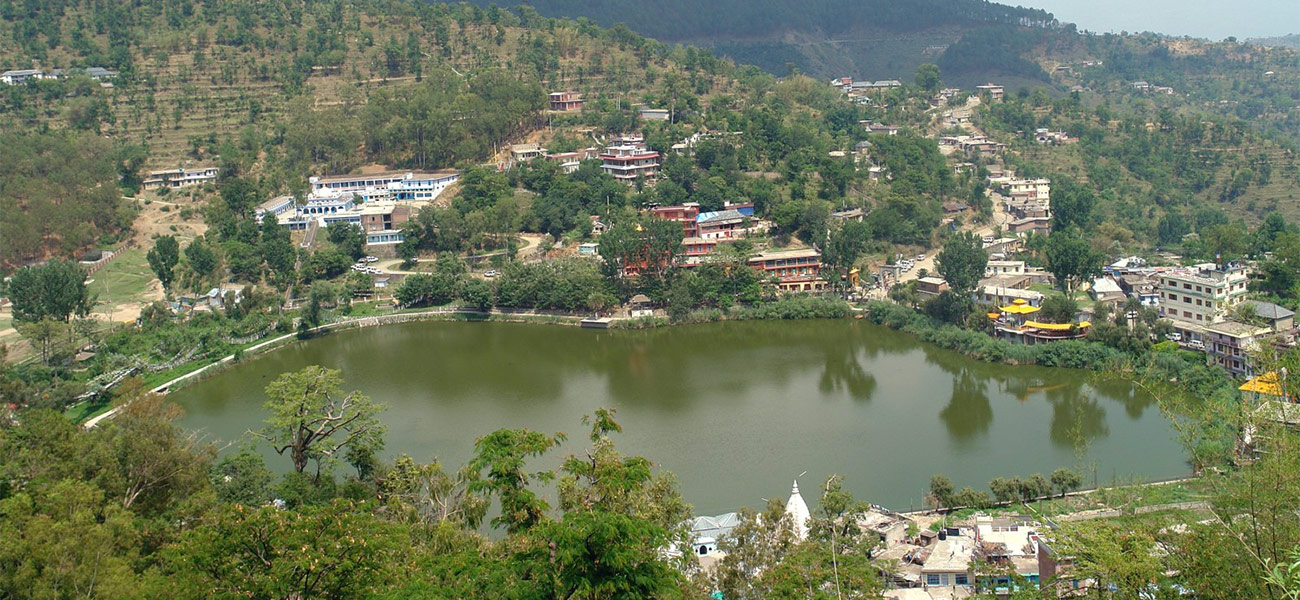
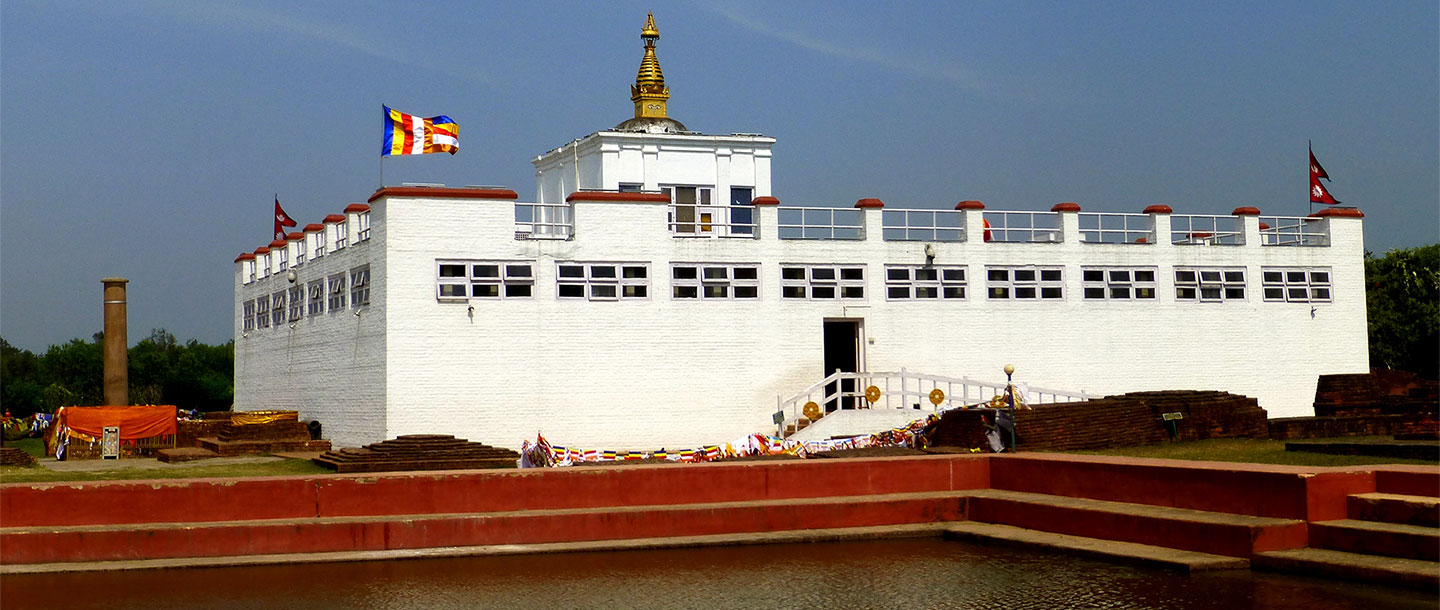
Sri Lanka Buddhist Trail Experience
14 Nights and 15 Days Sri Lanka Buddhist Trail Experience like never Before. Sri Lanka is a resilient Nation that follows Buddhist Philosophy. You will witness the Footprints of Lord Buddha, the Culture and Exotism of […]
Read Details English
English नेपाली
नेपाली








